Information for DietitiansClick below to view 4 short videos presented by Dr. Elizabeth Sussman PhD RD, Associate Professor of Nutrition and Dietetics specializing in renal nutrition and research, reviewing clinical data on the use of low protein diets supplemented with keto-analogues as a tool to slow the progression of CKD and maintain nutrition.  

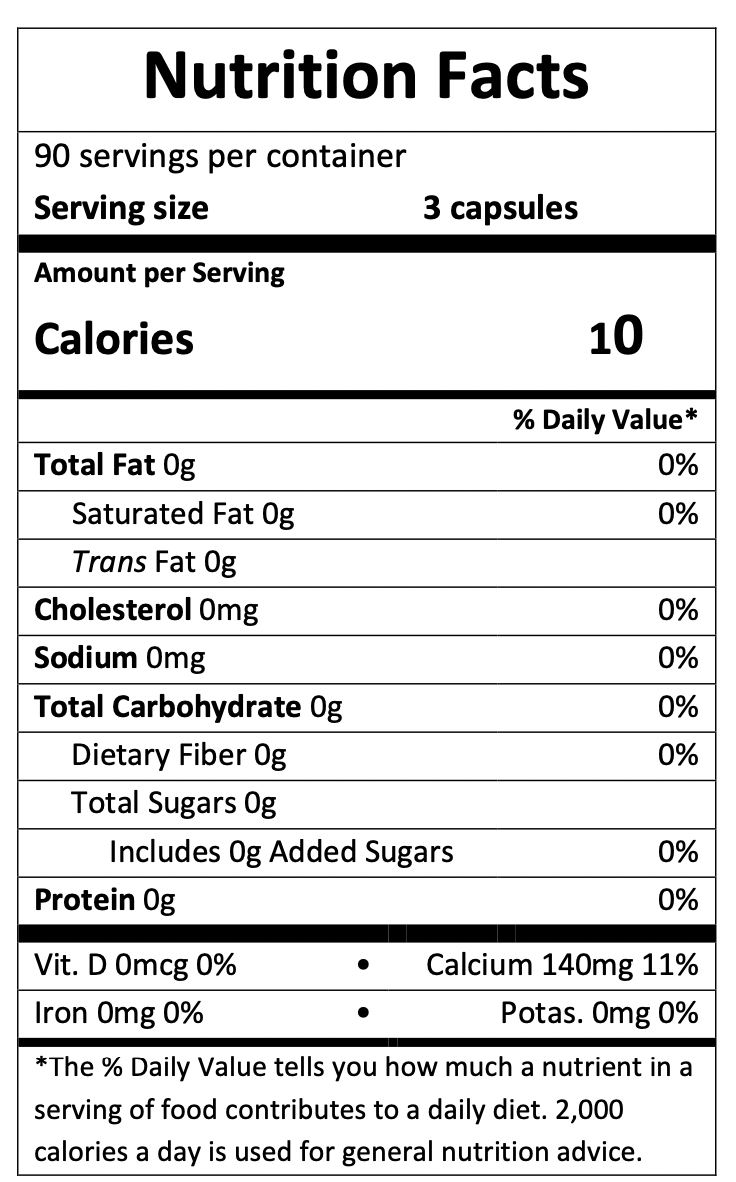
About KetorenaKetorena is a keto-acid analogue of essential amino acids (keto-analogue) used to maintain or improve nutrition and slow the progression of CKD for those on a low or very low protein diet.Each dose (3 capsules) of Ketorena contains 2100 mg or 2.1g of Keto & Amino Acids. 2.1g of ketorena offer 5.1 g protein when combined with a proper protein restricted diet.  
The 2020 KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline For Nutrition in CKD. Guideline 3 Protein and Energy Intake.Protein Restriction, CKD patients not on dialysis and without diabetes
Low protein diet or very low protein diet supplemented with a keto-analogue
Considerations of metabolically stable In the context of these recommendations, metabolically stable indicates: Find the full guideline here: KDIGO 2020 Nutrition in CKD guideline Ketorena DosingThe guideline states that there are two options to restricting protein to slow CKD as you can read above. The details of the guideline state that many people with CKD can live a healthy life while restricting protein to 0.55-0.60g of protein per kilo of body weight per day. This is considered a low protein diet or LPD. The guideline also states that to further reduce the decline in kidney function beyond the benefit of an LPD, a very low protein diet or VLPD of 0.28-0.43g of protein per kilo of body weight per day plus the addition of a keto-analogue is an option. To understand dosing let's start with an example: Julia weighs 130lbs. 130/2.2 = 59 Kg. 59 x 0.55 or 0.60 is about 32.5 or 35.5. So if Julia wants to protect her kidneys from further decline she should eat between 32.5g and 35.5g of protein per day. Let's say Julia is interested in slowing her CKD as much as she can so she wants to try a very low protein diet + Ketorena. 59 x 0.28 or 0.43 is about 16.5 or 25.5. With the VLPD Julia is protein deficient and needs to make it up with the low nitrogen low acid load Ketorena Keto-analogue. Ketorena is used to bridge the protein gap between the very low protein diet and the low protein diet while keeping the nitrogen and acid loads as low as possible. Each dose of Ketorena has 2.1g of Keto-analogue per dose which in combination with a proper VLPD offers 5.1g of protein. There is a very important distinction that has to be made: both LPDs and VLPDs have to be done properly. This is why we have a list lower down on this page of consultant renal dietitians who can help with a proper LDP or VLPD. Please remember Ketorena is a medical food an needs to managed under the care of a qualified health care provider. Let's go back to Julia. So Julia decides to use the VLPD and she eats 0.30g of protein per kg of body weight per day so she eats 17.7g. (59 x 0.30) . But the guideline indicates she needs 32.5g - 35.5g of protein per day. The gap filler is Ketorena. each dose offers 5.1g. So 5.1 x 3 doses per day = 15.3g. 17.7g from Julia's VLPD + 15.3g from Ketorena = 33g protein per day. Keto-Acid AnaloguesThe use of keto-analogues in combination with a low or very low protein diet is widely used for managing CKD in Europe, Asia and other parts of the world. Keto-analogue use has been limited in the United States because of its lack of availability here.When used with appropriate diet, keto-analogues have been shown to reduce CKD progression, slow the onset of uremic symptoms, and improve nutritional parameters and markers. Please see the section below titled: "Recent clinical Data on the use of keto-analogues with LPD/VLPD" for clinical references and further information. Keto-acid analogues of essential amino acids provide potential advantages for CKD patients. Ketoacids lack the amino group bound to the alpha carbon of an amino acid so they can be converted to their respective essential amino acids without providing additional nitrogen. Patient types who may benefit from a low or very low protein diet supplemented with Ketorena:
The following beneficial effects may be found with a keto-analogue supplemented protein restricted diet:
Recent clinical data on the use of keto-analogues with an LPD/VLPDClick on link to access.Ketoanalogues supplementation decreases dialysis and mortality risk in patients with anemic advanced chronic kidney disease. (Wu, Che-Hsiung et al. PLOS ONE May 5 2017)Effect of restricted protein diet supplemented with keto analogues in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta analysis. (Jiang, Zheng et al. Int Urol Nephrol 2016) Adherence to ketoacids/essential amino acids-supplemented low protein diets and new indications for patients with chronic kidney disease (Fouque et al. BMC Nephrology 2016) Keto Supplemented Low Protein Diet: A valid therapeutic approach for patients with steroid-resitant proteinuria during early-stage chronic kidney disease. (Zhang, J et al. J Nutr Health Aging 2016) Very low protein diet plus ketoacids in chronic kidney disease and risk of death during end stage renal disease: a historical cohort controlled study. (Bellizzi, V et al. NDT (2015)30:71-77) |